Isn’t it astonishing that most of the oxygen we rely on for our survival originates from the vast expanse of the ocean?
As Scuba divers, we understand and appreciate the value of oxygen like no one else.
Every time I go diving, I remember how grateful I am to be able to breathe oxygen on land without using any equipment.
While oxygen is vital for our existence, did you know that a significant part of comes from the ocean?
Phytoplankton produces around 50-85% of the oxygen
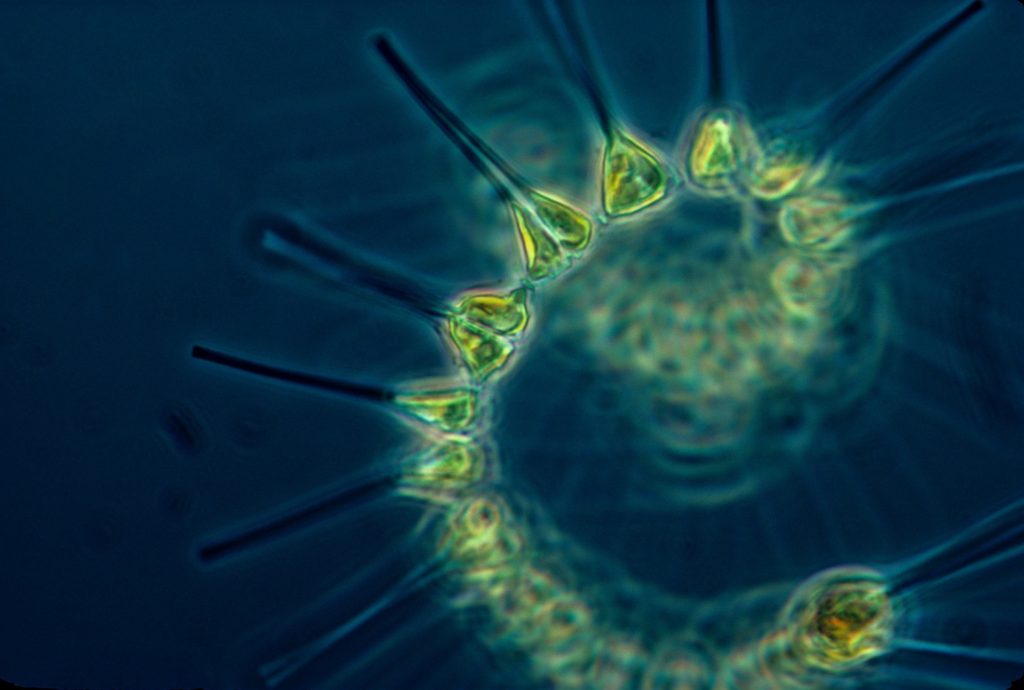
Most of the oxygen on earth is done through photosynthesis.
These tiny organisms play a crucial role in sustaining the oxygen levels in our atmosphere.
Additionally, there are other sources of oxygen. For example, there is an alga that coexists with coral and meteorites that contribute a small fraction.
A quick side note about something related but different: meteorites!
Believe it or not, meteorites bring all sorts of interesting elements to our planet!
For example, a metal called iridium, which is often used in wedding rings, may have come from meteorites. We can find evidence of meteorite impacts by looking at layers of rocks containing iridium. This metal is rare, and it’s even been linked to the extinction of dinosaurs during the Cretaceous period.
There’s also this super cool idea called the “panspermia theory.” It suggests that life on Earth might have come from outer space through meteorites. If you want to learn more, look it up! It’s a respected scientific hypothesis. They’re even studying this theory on space stations today.
If you think about photosynthesis, you usually picture beautiful tropical forests, tall trees, and wide grasslands. All these plants and trees release oxygen into the air.
But here’s the truth: around 50-85% of the oxygen we breathe comes from tiny phytoplankton.
(The percentage range may vary. it’s hard to measure exactly how much oxygen our planet produces.)
Scientists believe that phytoplankton is the first organism to make oxygen on Earth.
About 3.5 billion years ago, a specific type of phytoplankton called cyanobacteria kickstarted the whole photosynthesis process.
Back then, there weren’t any plants or animals on land. It was a barren era!
These amazing phytoplankton developed this cool trick called photosynthesis, which allows them to turn carbon dioxide and water into oxygen. This process created an environment that made it possible for us to live and thrive on land.
In the Antarctic Ocean alone, scientists estimate there are about 6 billion tons of phytoplankton. That’s a massive amount! To give you an idea, the entire 7.5 billion people human population adds up to about 340 million tons. So, the quantity of phytoplankton is roughly 20 times greater than all of us combined. It’s mind-blowing!
And that’s not all. When we think about all the oceans around the world, the number of phytoplankton living there is astronomical.
While we often focus on conserving and protecting the land, it’s important to take care of our oceans and their precious marine environment.
The ozone Layer is formed by the oxygen
The ozone layer is super important because it’s created by oxygen. Oxygen doesn’t just help us breathe; it also plays a crucial role in supporting life on land.
When oxygen molecules combine, they make up the ozone layer. This layer acts like a shield, protecting us from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
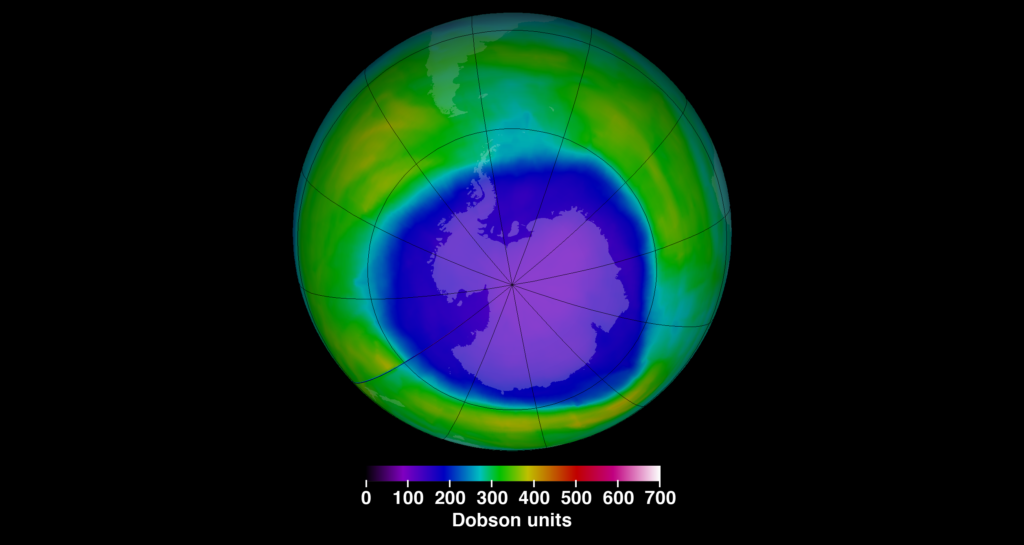
You might have heard about the “ozone” in the news, especially when people talk about the “ozone hole.”
The ozone layer forms when oxygen molecules collide with ultraviolet radiation.
Next, when ozone molecules interact with ultraviolet radiation, they change back into oxygen.
This ongoing process makes sure that the ozone layer blocks enough ultraviolet radiation from reaching the Earth’s surface.
Ultraviolet radiation is a big problem because it can harm our DNA, which is bad news for any living thing.
Without the ozone layer, our planet would probably be covered in huge barren areas. Even after 4.6 billion years since Earth formed.
We should be thankful to that incredible phytoplankton for producing oxygen. They help keep our planet and all of us healthy!
How deep can phytoplankton do photosynthesis?
Well, it depends on how clear the water is.
Usually, they can go about three times the water’s transparency, with a maximum of 150-200 meters range.
Once they go deeper than that, the light gets too weak for photosynthesis to happen.
In places like coral reefs with clear water, where you can see up to 50 meters, phytoplankton can still do photosynthesis even at 150 meters deep. But when there’s a red tide and the water gets all murky, even at that depth, it’s almost impossible for photosynthesis to occur.
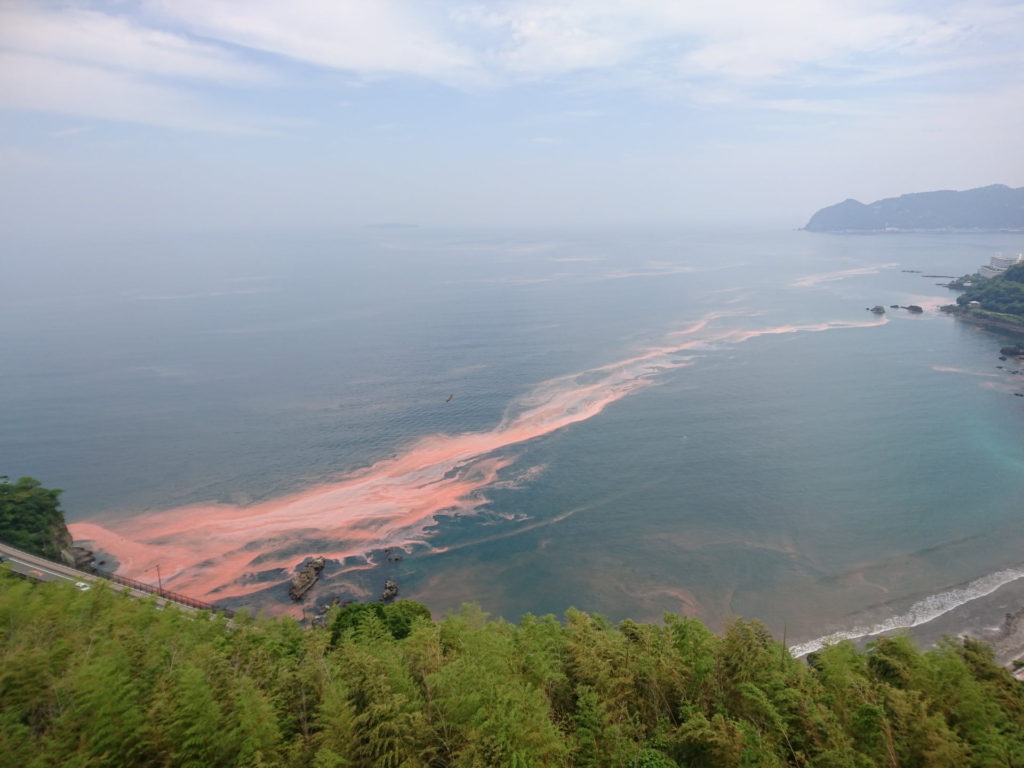

Lately, a growing concern about more frequent red tide events has been growing. So, let’s find out why they happen.
There are three big reasons why red tides are happening more often:
- The water is getting hotter.
- Too many nutrients are getting into the water, mostly from factories and homes.
- Unfortunately, there aren’t enough creatures that eat plankton like clams. The places where clams used to live, like tidal flats, are getting smaller. Without enough clams and other filter-feeding organisms, the water can’t get cleaned up.
Now, not all these problems are caused by humans alone. But if we keep damaging the Earth’s environment, it’s going to get worse. And if the phytoplankton starts to decline, our oceans could become “dead zones” where no fish or other creatures can survive. It’s a scary thought.
To sum it up:
- Phytoplankton are responsible for producing 50 to 85% of the oxygen we breathe!
- Thanks to phytoplankton, we can live on land and enjoy all the amazing things it has to offer.
- But the increase in red tides is making it tough for phytoplankton to do their job and perform photosynthesis.
Diving is such a fun experience! We get the chance to explore beautiful marine environments and ecosystems.
To take care of our planet, which is bursting with life, why not try living a little more eco-consciously?
Simple actions like turning off the shower while shampooing. Using less detergent when washing dishes can also make a big difference.
These small steps add up over time and can lead to significant changes.
By doing your part, you’ll not only help with conservation efforts but also help save money.
Let’s come together as divers to protect and preserve our incredible oceans.